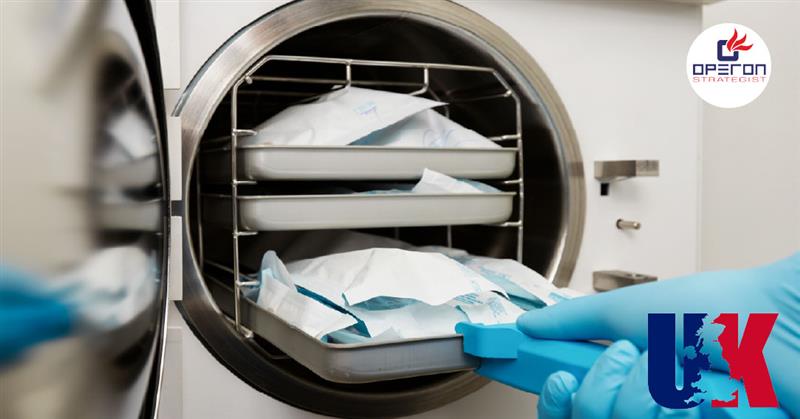
Sterilization is a critical process in the medical device manufacturing lifecycle. It ensures that devices are free from viable microorganisms and safe for patient use. In the UK, as in the rest of the EU, strict regulations govern medical device sterilization to ensure safety, compliance, and quality. Understanding the various medical device sterilization methods is essential for manufacturers aiming to meet MHRA and international standards such as ISO 11135, ISO 17665, and ISO 11737.
In this guide, we will explore the most commonly used medical device sterilization methods, their advantages and limitations, and how to choose the right method for your device.
Why Sterilization Matters in Medical Devices
Sterile medical devices are crucial in preventing Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAIs). Whether it’s a surgical instrument, catheter, or implant, ensuring it is sterile before use is a non-negotiable regulatory and ethical obligation.
Speak to a Regulatory Consultant Today
Regulators like the MHRA in the UK, and international standards such as the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) (EU) 2017/745, require manufacturers to validate and document sterilization processes during the product development lifecycle.
Common Medical Device Sterilization Methods
Below are the primary sterilization methods used in the UK medical device industry:
1. Ethylene Oxide (EtO) Sterilization
Overview:
EtO is a low-temperature gas-based sterilization method widely used for heat- and moisture-sensitive medical devices.
How it works:
Devices are exposed to ethylene oxide gas under controlled temperature and humidity. The gas penetrates packaging and materials, effectively killing microorganisms.
Advantages:
- Suitable for complex, heat-sensitive devices
- Effective against a broad range of microorganisms
- Penetrates through packaging and lumens
Limitations:
- Long aeration time to remove gas residues
- Requires special safety controls (EtO is toxic and carcinogenic)
- High setup and validation costs
Best for: Catheters, wound dressings, plastic instruments, electronics in devices
2. Steam Sterilization (Autoclaving)
Overview:
This high-temperature sterilization method uses pressurised steam and is among the oldest and most reliable sterilization techniques.
How it works:
Devices are subjected to steam at temperatures typically between 121°C and 134°C for a specific duration under pressure.
Advantages:
- Fast, effective, and low-cost
- No toxic residues
- Environmentally friendly
Limitations:
- Not suitable for heat- or moisture-sensitive devices
- May cause damage to electronics or some plastics
Best for: Surgical instruments, metal devices, reusable tools
3. Gamma Radiation Sterilization
Overview:
Gamma sterilization uses high-energy gamma rays, typically from Cobalt-60, to destroy microorganisms at the DNA level.
How it works:
Devices are irradiated with gamma rays in a controlled environment, achieving sterilization without raising the product temperature.
Advantages:
- Suitable for bulk sterilization
- Penetrates deep into materials
- Ideal for sealed and packaged products
Limitations:
- Material degradation possible over time
- Requires radiation safety compliance
- High infrastructure and handling costs
Best for: Single-use syringes, sutures, surgical gloves, tissue-based products
4. Electron Beam (E-Beam) Sterilization
Overview:
E-Beam sterilization is a form of ionizing radiation that uses a focused beam of high-energy electrons.
How it works:
The electron beam penetrates packaging and destroys microorganisms by breaking down their DNA.
Advantages:
- Faster than gamma sterilization
- No radioactive isotopes involved
- Environmentally safer than EtO
Limitations:
- Limited penetration depth
- Not suitable for dense or multilayer packaging
- High initial capital cost
Best for: Pharmaceuticals, diagnostic kits, lab consumables
5. Hydrogen Peroxide Plasma Sterilization
Overview:
A low-temperature sterilization technique using vaporised hydrogen peroxide gas and plasma to sterilize devices.
How it works:
The hydrogen peroxide gas diffuses into the device, followed by plasma generation which destroys microorganisms.
Advantages:
- Ideal for temperature-sensitive devices
- No toxic residues
- Short cycle time
Limitations:
- Limited penetration
- Not suitable for materials that absorb peroxide
- Equipment cost is high
Best for: Endoscopes, surgical devices with electronics, polymer-based instruments
How to Choose the Right Sterilization Method
Selecting the appropriate medical device sterilization method depends on various factors:
- Material Compatibility: Heat-sensitive materials may require EtO or plasma sterilization.
- Device Complexity: Devices with lumens or intricate components may not be suitable for radiation methods.
- Regulatory Requirements: Ensure the method complies with ISO 13485, ISO 11137, or ISO 14937, depending on the method chosen.
- Cost and Volume: High-volume products may justify gamma or E-Beam investment, while low-volume may benefit from outsourced EtO services.
- Packaging Considerations: Some sterilization methods require packaging that allows gas or radiation penetration.
Need Help with Sterilization Validation & Documentation?
Regulatory Requirements in the UK
In the UK, sterilization processes must comply with:
- UK MDR 2002 (as amended)
- ISO 13485:2016 (Quality Management System)
- ISO 11135 (EtO), ISO 11137 (Radiation), ISO 17665 (Steam)
- Validation and Revalidation protocols, with supporting documentation
Manufacturers are also expected to conduct routine biological indicators testing, maintain batch records, and submit sterilization data during conformity assessments or MHRA inspections.
📞 Need Help With Medical Device Sterilization Compliance?
At Operon Strategist, we provide comprehensive sterilization consulting, documentation, and validation support tailored for UK-based medical device companies. Whether you’re setting up your sterilization SOPs or preparing for MHRA audits, our experts are ready to guide you through every step.
Contact us today to discuss your project and ensure your sterilization process meets all UK and international standards.