US FDA 21 CFR 820.30 Design Control Requirements
What is US FDA 21 CFR 820.30 Design Control?
FDA 21 CFR Part 820.30 design control requirements is the most important stage in the advancement of a medical device since a defective plan may prompt it to be inadequate or dangerous (that is, not affirmed or cleared by the administrative organization). At the design stage, an outline design control process should be started and actualized as a feature of the Quality System Requirement. Generally, outline design controls are straightforward and logical steps to ensure that what you develop is what you meant to develop and that the last item lives up to your client’s needs and desires.

According to 820.30 guidance manufacturers of medical devices of Oman or from any other country should establish or maintain the plans that describes design and development activities
What is the Process of Design Control 21 CFR 820.30 for Medical Devices?
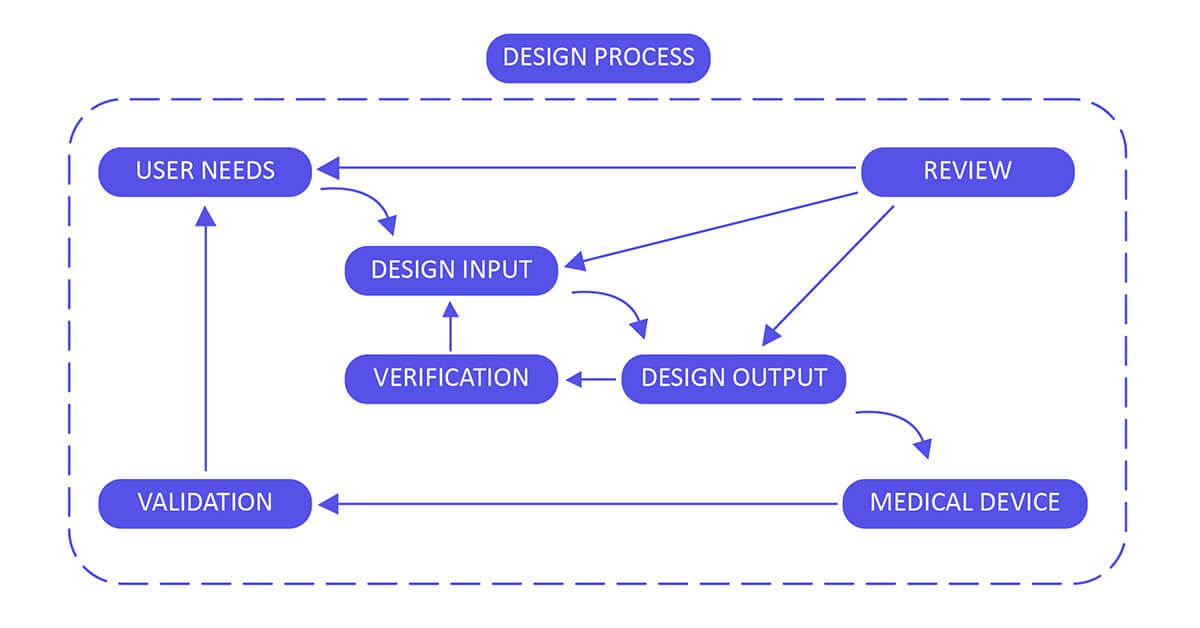
Design Control 21 CFR 820.30 Process for Medical Devices :
Build up and maintain a plan that describes the design and development activities and allocates the individual obligations for each activity. Guarantee you review, update and approve the plan until the device design is completed, verified and validated.
Let’s Connect! Your Queries, Our Expertise!
Design Input :
Utilize performance, safety, business economics, outputs of risk management and regulatory requirements as a basis to plan the device with the goal that its motivation and the proposed utilize are clear. The input may also come from surveying your customers( For example, clinicians, nurses, patients).
Design Output :
Design output methods or particulars need to stipulate or refer to the design input document developed by the team and need to identify the critical measures/outputs for the best possible capacity of the device. These incorporate the tests and strategies that may have been produced, adjusted or used to show conformance with the characterized configuration inputs. Examples of design outputs may include:
- The device itself.
- The user manual.
- Specifications A Risk Analysis Study results (For examples, validation and biocompatibility studies, storage).
- Technical Files.
Design Review :
Confirm the design, or identify at an opportune time and right any insufficiencies distinguished at other plan and improvement phases. Two common types of review are hazard analysis, and failure mode and effect analysis.
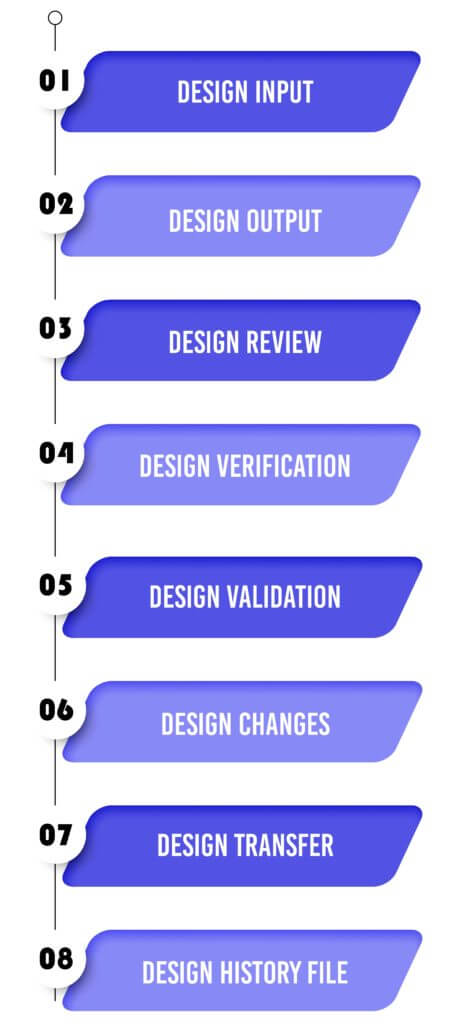
Design Verification :
Confirm the device outline by means of examination and target prove, verify that the design outputs meet the plan inputs. Design verification activities must be arranged and routinely analyzed and the outcomes must be documented.
Design Validation :
Approve the device design plan by means of examination and target prove, affirm that the last outline yield reliably meets the particular planned utilize. Design validation should follow successful design verification. Since outline check is directed while the plan work is being performed, design validation confirms that the medical device meets its intended use. Generally, this is set up through in vitro execution, practical testing, creature testing and additionally in vivo clinical assessments and trials.
Design Changes :
Guarantee that all plan changes are distinguished, documented, approved, verified, reviewed and endorsed before usage.
Design Transfer :
Ensure that the design of the medical device can be correctly translated into production specifications (that is, advancing successfully from product development to manufacturing).
Design History File :
The design history file (DHF) aggregates confirm (that is, the history of the design) that demonstrates that the outline was created as per outline of design control― specifically, the design and development plan, or the outline change design.
Operon Strategist the leading medical device regulatory consultant providing consultation for 21 CFR 820.30 design control with extensive experience and the practical implementation of design controls regulation for developing new design control processes or for making improvements to existing processes. For free consultation Contact us now.
We provide assistance to medical device manufacturer of Oman in design controls as per FDA and ISO 13485:2016 that can be mapped to the process that works best for the organization and the product being developed. If you need any help in setting up a design control system, or wish to modify an existing system in order to align with ISO 13485 or FDA design controls, feel free to contact us .
Get Your Design Process Assessed by Experts
FAQs
What is FDA 21 CFR 820.30 Design Control?
It’s a set of regulatory requirements established by the US FDA to ensure that medical device design and development processes are properly controlled and documented. It aims to ensure safety, effectiveness, and regulatory compliance.
Why is Design Control important for medical device manufacturers in Oman?
Implementing FDA-compliant design control helps Omani manufacturers meet international regulatory expectations, reduce product failures, and increase market access in the US, EU, and other regions.
Is design control required only for FDA approval?
No, it is also aligned with ISO 13485:2016 requirements. Even if not seeking FDA clearance, it is considered best practice for quality and compliance in global markets.
What is the Design History File (DHF) and why is it important?
The DHF contains documentation that proves the medical device was developed according to approved design control procedures. It is a key file reviewed during regulatory audits and inspections.
Can Operon Strategist assist with FDA 21 CFR 820.30 compliance?
Yes. Operon Strategist helps medical device manufacturers in Oman implement or enhance their design control systems in line with FDA 21 CFR 820.30 and ISO 13485:2016, ensuring readiness for audits and approvals.