Borderline Products: Medical Devices / Medicinal Products As Per MDR
New suggestions from the European Commission’s Medical Device Coordination Group provide better definitions for makers determining whether their things are medicines or devices (MDCG). It is straightforward to identify whether a product is a device covered by the Medical Devices Regulation 2017/745 or a drug covered by Directive 2001/83/EC on Community law linked to medicinal goods for human use (MPD).
Other items, such as medical devices that include a substance that would otherwise be designated a drug, aren’t always apparent whether they’re covered by the MDR or the MPD. By offering precise definitions of various types of products and clarifying how they differ, the new MDCG guideline document aims to clarify how developers may find a suitable regulatory framework for these so-called borderline scenarios.
Looking For a Medical Device Regulatory Consultant?
Let’s have a word about your next project
Definition:
Borderline products are ones for which it is unclear whether they come under MDR or MDP from the start. If the product is subject to MDR, it must comply with MD Article 2(1) and must not be within the scope of MDR Article 1(6).
Accessory of medical device Article 2(2) MDR
For a medical device to be considered an accessory, it must be employed in line with its original purpose or expressly and directly enhance the medical device’s medical functioning in terms of its desired uses.
Medicinal product (Article 1 (2) MDR)
Any chemical or combination of substances that is claimed to have the ability to treat or prevent illness in humans.
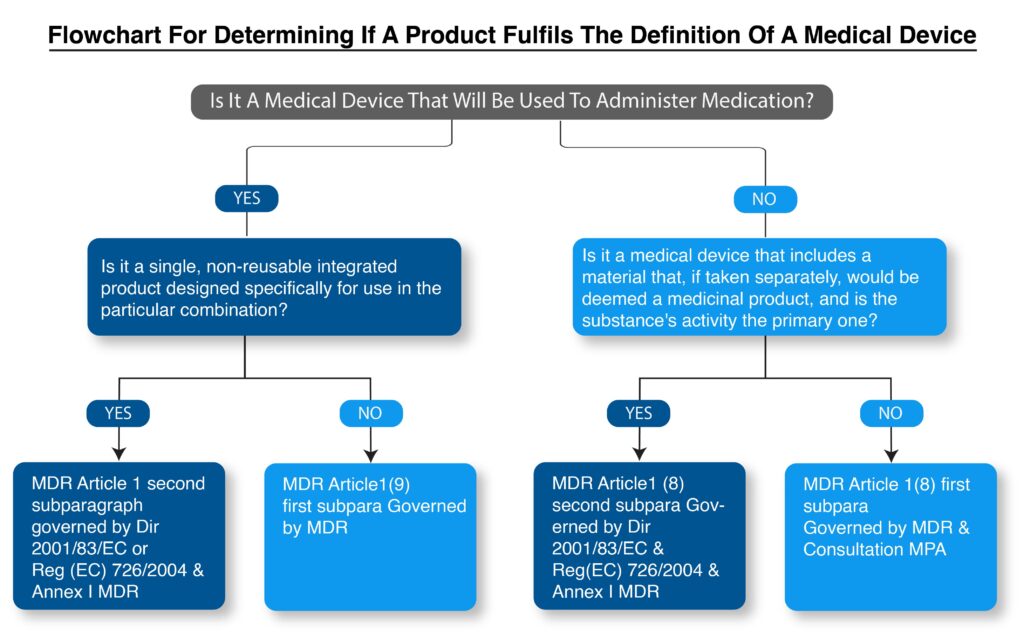
How to determine if a product fulfills the definition of a medical device as per MDR?
Flowchart for determining if a product fulfills the definition of a medical device.
Integral combinations of medical devices and medicinal products are governed as medicinal products:
This category includes devices designed to administer a medical product when the device and the combination of medications are merged into a single integral component that is intended only for use in the specified combination and is not reusable (MDR, Article 1(9) second subparagraph). It also covers devices that include a medicinal product as an integral element, and the medicinal item’s action is more important than the device’s (MDR, Article 1(8) second statement).
Some examples are integral medical devices and drug product combinations regulated as medicinal products.
- Aerosols containing a medicinal product
- Nebulisers pre-charged with a specific medicinal product
- Patches for transdermal drug delivery
- Syringes prefilled with a medicinal product
Medical device for administering pharmaceutical products
This category specifically pertains to devices meant to distribute a medical product under the MPD but are not fundamental to the medicinal product.
In this case, the MDR applies to the device regardless of the medical product restrictions outlined in Directive 2001/83/EC.
Examples of medical devices for the administration of medicinal products
- Drug delivery pumps
- Implantable infusion pumps
- Reusable iontophoresis devices
Medical devices incorporating, as an essential component, an ancillary medicinal product
The MDR defines medical devices that include a substance that, when used separately, would be considered a medicinal product under Article 1 of the MPD. This includes medicinal products derived from human blood or plasma, with a secondary action to the device’s primary action.
For the sake of convenience, these are referred to in this article as devices that incorporate an auxiliary medical product as an integral component. This includes natural medication.
Examples of medical devices incorporating, as an integral part, an ancillary medicinal product
- Catheters coated with heparin or an antibiotic agent
- Bone cement containing antibiotics
- Root canal fillers which incorporate medicinal products with ancillary action to that of the device
- Soft tissue fillers incorporating local anesthetics
- Bone void filler containing growth factors
- Condoms coated with spermicides
- Electrodes with steroid-coated tip
- Wound dressings, surgical or barrier drapes (including tulle dressings) with antimicrobial agent
- Intrauterine contraceptives containing copper or silver
Operon Strategist offers cost-effective, high-quality regulatory services tailored to your needs. With expert guidance in product classification and CE mark compliance, we ensure error-free deliverables worldwide. Contact us to discuss your requirements today!