Suture Manufacturing:
Paying close attention to detail and adhering to tight quality control procedures are essential when manufacturing surgical sutures. To maximize wound healing and scar aesthetics, surgeons choose the best suture materials for tissue approximation. The choice of sutures and needles varies widely across surgeons, and awareness of the numerous possibilities available enables doctors to form their preferences.
What is Surgical Suture?
Surgical suture is an equipment used to hold bodily tissues together and round the edges of cracks following surgery or damage. A needle with a length of thread attached is used to apply sutures, and there are numerous varieties with different needle form, size, and thread composition.
Looking For a Medical Device Regulatory Consultant?
Let’s have a word about your project
Device Design and Other Characteristics of Suture
Medical threads called surgical sutures are used to repair wounds. They can be non-absorbable (need to be removed) or absorbable (body breaks them down over time). Stainless steel suture needles are engineered to be robust, thin, and sharp. Depending on the surgical process, the design changes.
Sutures’ strength, also known as tensile strength, or how well they withstand pulling structures, as well as whether they are absorbable, are important aspects to note.
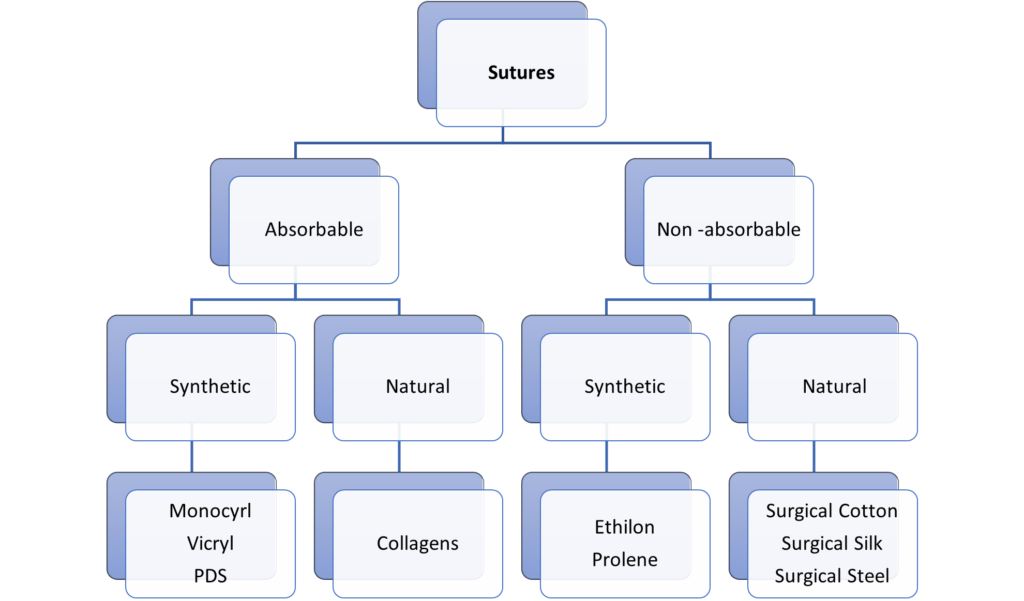
Sutures Material and its Classification -
Without expert guidance, it is difficult to start a surgical suture manufacturing business. Contact us right away to receive all the market information needed to begin producing sutures. You can also get assistance with the process of regulatory compliance, like CDSCO Manufacturing License, FDA 510(k), CE Marking and so on, from Operon Strategist.
What are the Types of Surgical Sutures?
Based on absorbability, absorbable sutures do not require removal because the body breaks them down over time. Catgut, Polydioxanone (PDS), Polyglactin (Vicryl), and Polyglycolic Acid are a few examples. On the other hand, Non-absorbable Sutures can either be removed later or left in place permanently because they cannot be absorbed by the body. Silk, Nylon, Polyester, and Polypropylene are a few examples1.
Based on origin, natural sutures are sourced from biologically based natural fibres. Silk and catgut sutures are two examples. Whereas Synthetic sutures are produced through chemical synthesis. Examples include PDS1, Nylon, and Polyester.
Lastly depending on Structure, Multifilament or braided sutures are made of numerous small threads that have been braided together as opposed to monofilament sutures, which are made of a single thread.
Take the Next Step Towards Suture Manufacturing Now and Let’s Turn Your Vision Into Reality!
What is the Use of Surgical Sutures?
Surgical sutures not only help to mend damaged tissues and close surgical incisions, but they also help to stop bleeding and close wounds. Whether they are used in sophisticated organ transplant surgeries, delicate ophthalmology treatments, or basic wound closures, sutures are crucial to the success of medical interventions. Their choice is determined on the type of tissue, the location, and the surgical prowess, exhibiting their flexibility to meet various therapeutic needs.
Start Your Surgical Suture Manufacturing Project with Operon Strategist
Looking to set up your medical device manufacturing facility for surgical sutures? Trust Operon Strategist, a leading medical device regulatory consultant, with over 12 years of expertise and a global footprint across 32 countries. Our Turnkey Project Solutions ensure seamless setup, while our focus on quality assurance guarantees regulatory compliance and license acquisition. Let us help you bring your vision to life. Contact us now to kickstart your manufacturing journey.
Visit Our Manufacturing Blogs for More Information.

-
Operon Strategisthttps://operonstrategist.com/author/snehal/
-
Operon Strategisthttps://operonstrategist.com/author/snehal/
-
Operon Strategisthttps://operonstrategist.com/author/snehal/
-
Operon Strategisthttps://operonstrategist.com/author/snehal/




