Introduction to Blood Collection Tube Manufacturing
Blood collection tube manufacturing is a critical process in the medical and diagnostic industry. Blood collection tubes, commonly called vacutainers, are sterilized glass or plastic tubes designed to collect, store, and preserve blood samples. They often contain additives that maintain the integrity of specific blood components for accurate testing.
The colored rubber stoppers on the tubes indicate the type of additive used, ensuring proper sample handling. Using the wrong tube can compromise test results, highlighting the importance of precise manufacturing and strict quality control. Modern blood collection tubes may include gel barriers, clot activators, or anticoagulants, which are essential for laboratory procedures such as serum separation, hematology analysis, and biochemistry testing.
Looking for Medical Device Regulatory Consultant?
Let’s have a word about your project
Want to elevate your blood collection tube manufacturing project? Contact Operon Strategist today for expert guidance on manufacturing plant layout design and turnkey solutions that can transform your blood collection tube manufacturing process.
Types of Blood Collection Tubes
Understanding the different tube types is essential for both manufacturers and laboratories:
- No Additive Tube:
- Used for general blood collection.
- Provides uncontaminated serum for biochemistry, serology, and other clinical tests.
- Used for general blood collection.
- Serum Blood Collection Tube:
- Designed to provide high-quality serum.
- Includes tubes with or without clot activators.
- Typically has a brick-red cap.
- Designed to provide high-quality serum.
- Hemo Repellent Coated Tube:
- Coated with silicon to prevent blood cells from adhering to the tube wall.
- Ensures rapid coagulation and accurate biochemical testing.
- Coated with silicon to prevent blood cells from adhering to the tube wall.
- Gel + BCA Tube:
- Contains a barrier gel at the bottom.
- Separates serum from cells after centrifugation without mixing additives.
- Contains a barrier gel at the bottom.
- Whole Blood Collection Tube:
- Used for hematology tests.
- Includes EDTA K2/K3 tubes for blood cell analysis and ESR tubes for anticoagulation testing.
- Used for hematology tests.
- Plasma Blood Collection Tube:
- Ensures high-quality plasma samples.
- Used in clinical laboratories for diagnostic purposes.
- Ensures high-quality plasma samples.
- No Additive Tube:
Blood Collection Tube Manufacturing Process
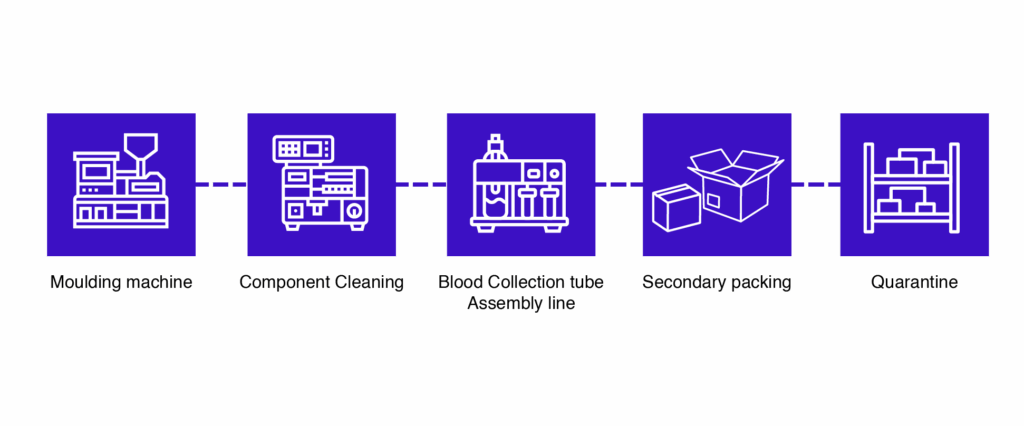
The manufacturing process involves multiple stages, each critical to product quality and compliance.
1. Tube Molding
- Small plastic tubes are produced using molding machines, either electric or hydraulic.
- Uniform tubes are essential for accurate blood collection and laboratory testing.
2. Component Cleaning
- All components are cleaned to remove contaminants before assembly.
- Electroplating or surface finishing requires clean components for proper adhesion and quality.
3. Assembly Line
- Blood collection tubes are assembled on automatic or semi-automatic assembly lines.
- Standard throughput: up to 200 tubes per minute.
- Steps include tube feeding, stopper insertion, additive dosing, and labeling.
4. Sterilization
- Ensures all tubes are free from bacteria and viruses.
- Methods include gamma radiation, EtO, or steam sterilization depending on material type.
5. Quarantine (Finished Goods Store)
- Tubes are stored temporarily to ensure no defective or contaminated products reach the market.
Quality checks are performed before distribution.
Blood Collection Tube Manufacturing Machinery
- BCT Cap and Stopper Combination Machine: Inserts rubber stoppers precisely into tubes.
- Labeling Machine: Applies labels for identification and traceability.
- Dosing Machine: Automatically adds liquid additives or reagents.
- Capping Machine: Secures plastic or metal caps and ensures tight seals.
- Centrifuge Machine: Separates blood components efficiently.
- Shrink Packaging Machine: Protects tubes with PE, POF, or PVC shrink films.
Quality Standards and Regulatory Compliance
- Blood collection tube manufacturing is highly regulated:
- Compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 820 and ISO 13485 is mandatory.
- Detailed documentation and traceability ensure quality and meet regulatory standards.
- Proper packaging, labeling, and sterilization maintain tube integrity until clinical use.
Market Insights for Blood Collection Tubes
- Global demand is increasing due to rising healthcare awareness and diagnostic testing.
- Technological advancements in blood collection and processing expand opportunities for manufacturers.
- Training and availability of skilled healthcare professionals enhance market growth.
- Emerging trends include gel-barrier tubes, additive innovations, and automated manufacturing solutions.
Ready to Launch Your Blood Collection Tube Manufacturing Unit?
Role of Operon Strategist in Blood Collection Tube Manufacturing
Operon Strategist supports manufacturers in:
- Plant Layout & Turnkey Solutions: Optimize production efficiency.
- Regulatory Guidance: Ensure FDA, ISO, and CE compliance.
- Process Optimization: From molding and assembly to sterilization and packaging.
- Quality Assurance: Implement rigorous QC measures and documentation for traceability.
Our team helps manufacturers produce high-quality, compliant blood collection tubes ready for domestic and international markets.
Get Your Free PDF Guide Now
Visit Our Manufacturing Blogs for More Information.
FAQs
What is medical device manufacturing?
It involves designing, developing, producing, and testing medical devices such as blood collection tubes, catheters, syringes, and implants to meet stringent quality and regulatory requirements.
Which regulations apply to medical device manufacturing?
Key regulations include FDA 21 CFR Part 820 (Quality System Regulation), ISO 13485 (Quality Management System), and region-specific approvals such as CE Marking, CDSCO in India, and EMA guidelines.
What is the difference between Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC)?
QA focuses on systemic processes to prevent defects, while QC involves inspection and testing of finished products to ensure they meet specifications.




