Introduction: Why Surgical Sutures Matter
Did you know that the global surgical suture market is projected to reach $5.1 billion by 2027? As a critical component in wound closure, surgical sutures directly influence surgical outcomes by minimizing complications, reducing infection risks, and supporting faster recovery.
For manufacturers, producing high-quality surgical sutures is not just about meeting demand—it’s about ensuring safety, compliance, and global market readiness.
What Are Surgical Sutures?
A surgical suture is a medical device used to hold tissues together after surgery or injury. Each suture consists of a needle attached to a surgical thread, available in multiple sizes, shapes, and materials. Surgeons select sutures based on:
- Wound type
- Tissue location
- Healing duration
Looking For a Medical Device Regulatory Consultant?
Elevate your surgical suture manufacturing with Operon Strategist. Contact us today for expert guidance on plant layout design and turnkey solutions tailored to enhance efficiency and compliance
Functions of Surgical Sutures
Surgical sutures serve multiple purposes in clinical practice:
- ✅ Closing surgical incisions
- ✅ Promoting tissue healing
- ✅ Minimizing bleeding
- ✅ Reducing scar formation
Suture Materials and Their Classification
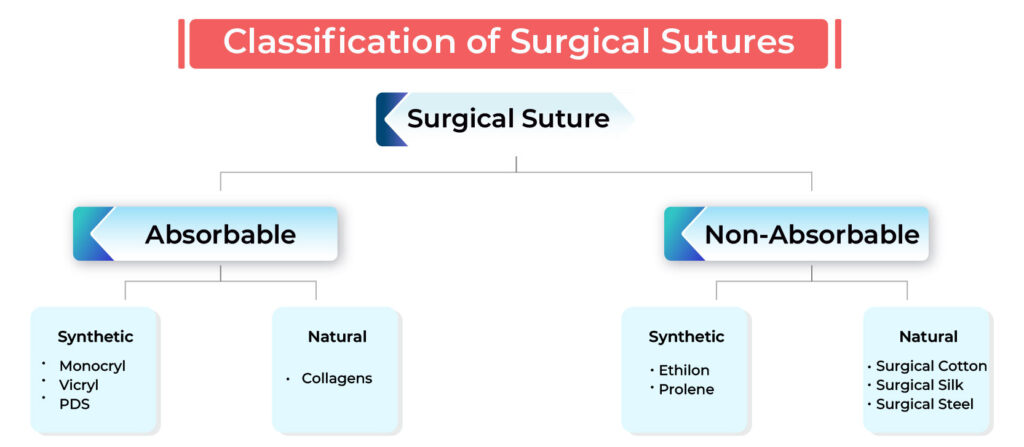
Sutures are classified based on absorbability, origin, and structure:
- Absorbability
- Absorbable Sutures (dissolve naturally) → Catgut, Polyglactin (Vicryl), Polydioxanone (PDS), Polyglycolic Acid (PGA)
- Non-Absorbable Sutures (require removal or remain permanently) → Silk, Nylon, Polyester, Polypropylene
- Origin
- Natural Sutures → Silk, Catgut
- Synthetic Sutures → Nylon, PDS, Polyester
- Structure
- Monofilament Sutures → Smooth, single-thread, lower infection risk
- Multifilament Sutures → Braided, strong tensile strength, better knot security
Confused about choosing the right suture material? Consult the Operon Strategist for expert guidance tailored to your facility.
Start Your Suture Manufacturing Journey Today!
Key Characteristics of Surgical Sutures
To meet medical standards, sutures must demonstrate:
- Tensile Strength → Ability to withstand wound tension
- Absorption Rate → Gradual degradation (absorbable) vs permanence (non-absorbable)
- Needle Design → Straight or curved, round-bodied or cutting-edge, varying in size and length
Surgical Suture Manufacturing Process
Manufacturing surgical sutures involves precision engineering and strict compliance with regulatory guidelines. The key steps include:
- Material Selection → Choosing the right thread and needle materials
- Sterilization → Ensuring complete contamination control
- Coating & Processing → Enhancing performance with antimicrobial coatings
- Packaging → Secure, sterile, and durable packaging for safe use
- Quality Control → Comprehensive testing to meet global standards
Regulatory Compliance & Licensing 📜
To sell surgical sutures in the global market, manufacturers must comply with regulatory guidelines such as:
- India: CDSCO Manufacturing License
- USA: FDA 510(k) Clearance
- Europe: CE Marking under EU MDR
- Other Markets: ISO 13485 Certification for QMS Compliance
Need help obtaining medical device approvals? Contact Operon Strategist for hassle-free licensing!
Transform your vision into a compliant and profitable surgical suture manufacturing unit.
Start Your Manufacturing Journey with Operon Strategist
Looking to establish a state-of-the-art surgical suture manufacturing facility? Operon Strategist is your trusted partner for:
✅ Turnkey Project Consulting – From feasibility to execution.
✅ Regulatory Compliance Support – CDSCO, FDA, CE Marking approvals.
✅ Plant Layout & Process Optimization – Efficient workflow design.
✅ Quality Assurance & Training – Meet global safety standards.
🔴 Partner with Operon Strategist and turn your vision into reality!
📞 Contact us today!
Surgical Suture Manufacturing - Get Your Copy in PDF
FAQs
What are the main types of surgical sutures?
Sutures are classified as:
Absorbable vs Non-Absorbable (based on whether they dissolve in the body)
Natural vs Synthetic (based on material origin)
Monofilament vs Multifilament (based on thread structure)
Why is regulatory compliance important in suture manufacturing?
Compliance ensures safety, effectiveness, and global market acceptance of the product. Non-compliance can lead to rejection, recalls, or penalties.
What materials are commonly used for absorbable sutures?
Common absorbable materials include Catgut, Polyglactin (Vicryl), Polydioxanone (PDS), and Polyglycolic Acid (PGA).




